JWT attacks
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are commonly used for authentication, session management, access control, and securely exchanging data between web applications. They are also widely used in API access, OAuth 2.0 flows, and Single Sign-On (SSO) implementations. However, poor implementation of JWTs can introduce serious security risks and may be exploited to compromise a web application.
Specs define JWT: RFC7519
JWT Format
Section titled “JWT Format”A JWT consists of three parts, separated by dots:
HEADER.PAYLOAD.SIGNATURE- HEADER: Define the type(
typ) of token and the signing algorithm (alg) (e.g.HS2456) - PAYLOAD: Contains claims about the user, session, or other data (e.g.
{"user": "user1", "admin": false}). Common claims:- Issuer (iss)
- Subject (sub)
- Audience (aud)
- Expiration time (exp)
- Not before (nbf)
- Issued at (iat)
- JWT ID (jti)
- SIGNATURE: A cryptographic signature that ensures the token hasn’t been tampered with. Each part is Base64URL-encoded (without padding) and concatenated with a dot:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyMSIsImFkbWluIjpmYWxzZX0.X5cBA0klC0df_vxTqM-M1WOUbE8Qzj0Kh3w_N6Y7LkIJSON Web Algorithms (JWA)
Section titled “JSON Web Algorithms (JWA)”JWT algorithms are defined in[JWA Specifications](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7518 Common JWT Signing Algorithms
- Symmetric algorithms (HMAC based using a shared secret):
HS256,HS384,HS512 - Asymmetric algorithms (public/private key):
RS256(RSA based),ES256(Elliptic Curve based),PS256(RSA based with MGF1 padding), etc. - None: A non-algorithm that implies no signature (insecure and should never be used) More algorithms at RFC 7518
Signing a token:
signature = ALGORITHM.Sign(header + "." + payload, key)Verifying a token:
ALGORITHM.Verify(signature, header + "." + payload, key)XXE Attack
Section titled “XXE Attack”- Signature not verified
- Unsigned JWT
- Weak Signing Key
Mitigation
Section titled “Mitigation”- Always use a library’s verify() method before accessing claims.
- Never trust the payload until the signature is successfully validated.
- Explicitly disable the “none” algorithm in your JWT library configuration.
- Do not rely on defaults, enforce algorithm allowlists like
RS256orHS256.
Exploit
Section titled “Exploit”Signature not verified
Section titled “Signature not verified”JWTs are not encrypted by default, which means their contents can be viewed and even modified by anyone. To ensure the token hasn’t been tampered with, applications must validate the signature. However, some applications skip this critical step, allowing attackers to modify the payload and exploit the system with ease.
- Get a valid JWT token.
- Decode the Base64URL-decode to see header and payload
- Make changes to the payload, like changing to a different user.
{ "iss": "portswigger", "exp": 1747553975, "sub": "john"}Change user:
{ "iss": "portswigger", "exp": 1747553975, "sub": "admin"}- Base64URL-encode the header and payload.
- Send with original signature, if the application does not verify the signature you’ll be authenticated as
adminuser.
Unsigned JWT
Section titled “Unsigned JWT”Early versions of many JWT libraries accepted None or none as a valid option, meaning the token was considered valid without a signature at all.
- Use burpsuite JSON Web Token extensions to remove the signature.
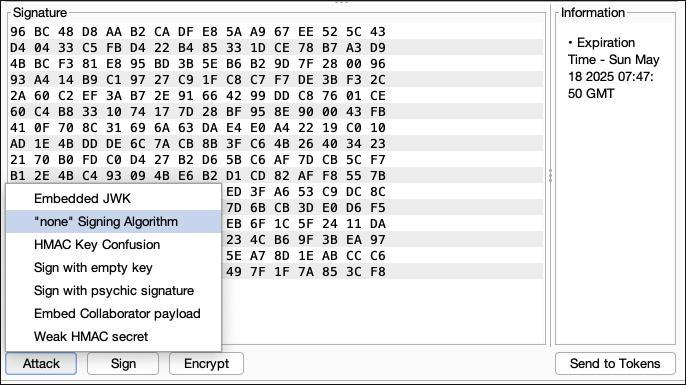
- It removes the signature. The header now looks like from this:
{ "typ": "JWT", "alg": "HS256"}to this:
{ "typ": "JWT", "alg": "none"}- JWT with no signature:
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJpc3MiOiJwb3J0c3dpZ2dlciIsImV4cCI6MTc0NzU1NDQ3MCwic3ViIjoid2llbmVyIn0.- Send the token if the application does not reject
"alg": "none", it will accept the token as valid.
Weak signing key
Section titled “Weak signing key”HMAC-based algorithms rely on the strength of the secret key. If the key is weak or easily guessable, an attacker can brute-force it and generate their own valid tokens, effectively bypassing authentication.
Use hashcat to try to brute-force the secret key.
hashcat -a 0 -m 16500 eyJraWQiOiI0ODY2MTZhOC1lM2I0LTQzZWItODQ3Mi04NTc1OTgzNWJhNTkiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJwb3J0c3dpZ2dlciIsImV4cCI6MTc0NzU1NDc1NSwic3ViIjoid2llbmVyIn0._75lGMCWEJRNqs-mH0KCZ4IDodeS3IEQFPhUZOGKDNk rockyou.txtList of known JWT secrets: wallarm/jwt_secrets
Create a new signing key with the cracked secret key.
- Burp Suite > JWT Editor > New Symmetric Key
- Specify secret > Generate
- Go to JSON Web token, change the payload and sign with new key.
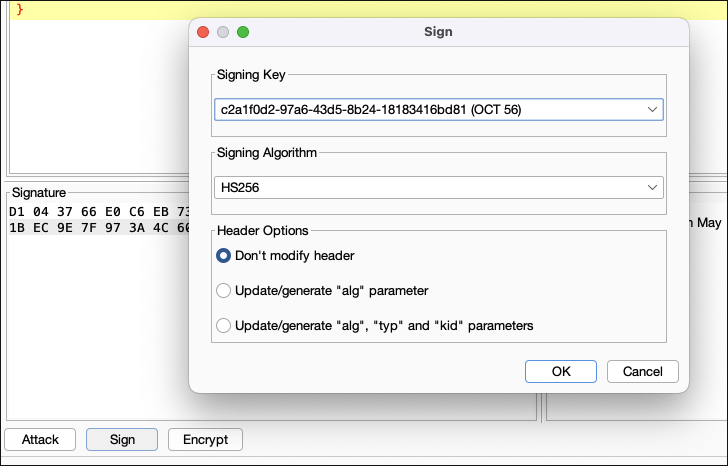
Algorithm Confusion (RSA to HMAC)
Section titled “Algorithm Confusion (RSA to HMAC)”TODO
Algorithm Confusion (ECDSA to HMAC)
Section titled “Algorithm Confusion (ECDSA to HMAC)”TODO
kid Injection (Key ID Manipulation)
Section titled “kid Injection (Key ID Manipulation)”TODO
Embedded JWK (CVE-2018-0114)
Section titled “ Embedded JWK (CVE-2018-0114)”TODO
JKU / X5U Header Abuse
Section titled “JKU / X5U Header Abuse”TODO
CVE-2022-21449 (Psychic Signature)
Section titled “ CVE-2022-21449 (Psychic Signature)”TODO
